Use the actual Eliza algorithm in your chatbot
Even though the chatbot trend is fairly new, they've been around for a long time. I can remember talking to chatbots over ten years ago when trying to reach out to my mobile phone services (spoiler alert: I never got hold of them ~~).
And then in 2016, Mark Zuckerberg announced the integration of chatbots on Facebook Messenger and the trend started. But how did all this start?
The first significant chatbot ever created was Eliza. It is a program, part of the early work in NLP (Natural Language Processing). Developed between 1964 and 1966, it was a state-of-the-art NLP program back then, had to run on 128kb of ram (that was a lot back in 1966!). Eliza has a single purpose: keep the conversation running by asking questions to the user and trying to get him/her to keep talking. Eliza was actually meant to simulate the conversation of a psychotherapist.
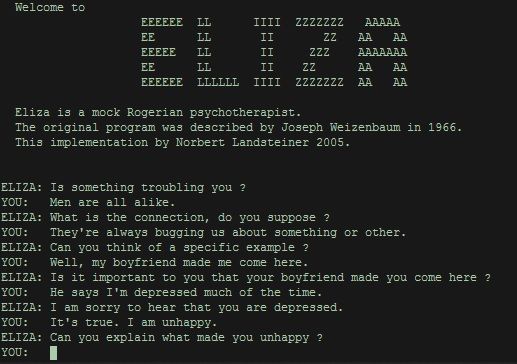
Let's see how to integrate the Eliza algorithm into a CSML chatbot!
tl;dr: You can import the chatbot with the Eliza integration, by clicking on the link at the bottom of the page... and yes it's free.
Step 1: The use case
We're going to create a chatbot that will interact with people who want to chitchat or are feeling a little down.
This chatbot will:
- propose a meditation video
- give a random motivational quote
- talk to the user using the Eliza algorithm
Step 2: Let's create the video and quote conversation
For the sake of simplicity, we'll create this chatbot in the CSML Development Studio, it's free, and easy to use and I can share the chatbot at the end 🤙
start:
say "Hello, I'm your Elizo"
say Typing(3000)
say "I'm here to make you feel good 🤗"
say Typing(3000)
goto menu
menu:
say Question("What would you like to do?",
buttons=[
Button("I want to meditate") as btn_med,
Button("I need some motivation!") as btn_mot,
Button("Let's talk") as btn_talk
])
hold
if (event match btn_med) {
goto meditation
} else if (event match btn_mot) {
goto motivation
} else {
say "Tell me what's on your mind ☺️"
goto talk
}
meditation:
say "Here is video to help you with your meditation, enjoy 😌"
say Video("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=inpok4MKVLM")
say Typing(20000)
goto menu
motivation:
do quotes = HTTP("https://type.fit/api/quotes").get().send()
do shuffledQuotes = Shuffle(quotes)
say Typing(3000)
say "“{{shuffledQuotes[0].text}}”\n\n_{{shuffledQuotes[0].author}}_"
say Typing(8000)
goto menu
In the code above, we show three buttons to the user, the meditation step shows a video, and the motivation step gives a motivational quote provided by an -awesome- API. Both of these steps bring the user back to the menu at the end.
Step 3: Integrate Eliza
In order to use the Eliza algorithm, we'll need to add it to our list of custom functions.
First, let's find a version of the algorithm that we can use. CSML supports a large range of languages such as NodeJS, Python, Java, Go, etc... I am more of a NodeJS guy myself so I found this repository that seems to do the job.
Let's open a new NodeJS project, install the elizanode dependency using npm and create an index.js file.
$ mkdir eliza-csml && cd eliza-csml
$ npm init -y
$ npm i --save elizanode
$ touch index.js
You now should have an index.js with the elizanode dependency. Let's wrap it so we can upload it as custom function. In order to do that we're going to edit index.js
// We import the dependency
const ElizaNode = require('elizanode');
exports.handler = async function handler(event) {
// event.query encloses the user message
if (!event.query) return { error: 'No query parameter' };
// We init Eliza
const eliza = new ElizaNode();
// We get the answer from eliza
const reply = eliza.transform(event.query);
// We check if Eliza evaluates the user message as the end of the conversation
if (eliza.quit) {
return { end: true, message: reply };
}
return { end: false, message: reply };
};
And finally, we need to zip the package:
$ zip -r9 eliza.zip index.js node_modulesAnd now let's import it into the Studio:
- Click on
Functionsin the sidebar, thenAdd custom function>Quick Mode - Click on the upload area and upload the file eliza.zip that you just created
- Give a name to your function
- Make sure that the runtime is set to
nodejs12.x - Double check that the handler is
index.handler
We're all set!
Step 4: Get Eliza to interact with the user
Let's now add the missing step to this chatbot: the talk step!
talk:
hold
do response = Fn("Eliza", query=event)
say Typing(5000)
say "{{response.message}}"
if (response.end == true) {
goto menu
}
goto talk
This step is basically an infinite loop: as long as Eliza does not detect that the user wants to end the conversation, we keep querying the algorithm so Eliza can answer. Note that a simple "Bye" can end the conversation at any given time, the user then goes back to the menu.
Step5: Done!
That's it! We can now test Eliza 🎉
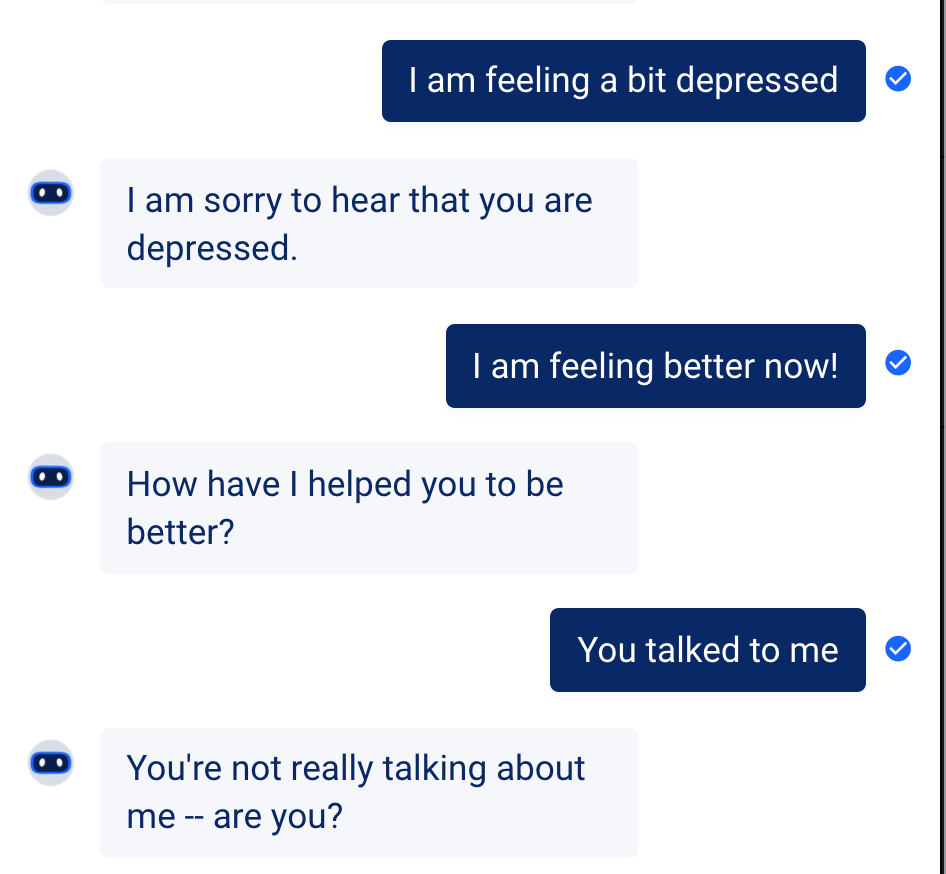
You can obviously add a few features to this chatbot, like adding more NLP to it or extending Eliza's vocabulary.
To import the ready-to-use chatbot, 👉 it's over here 👈.





